MATLAB semilogy in MATLAB®
Learn how to make 9 semilogy charts in MATLAB, then publish them to the Web with Plotly.
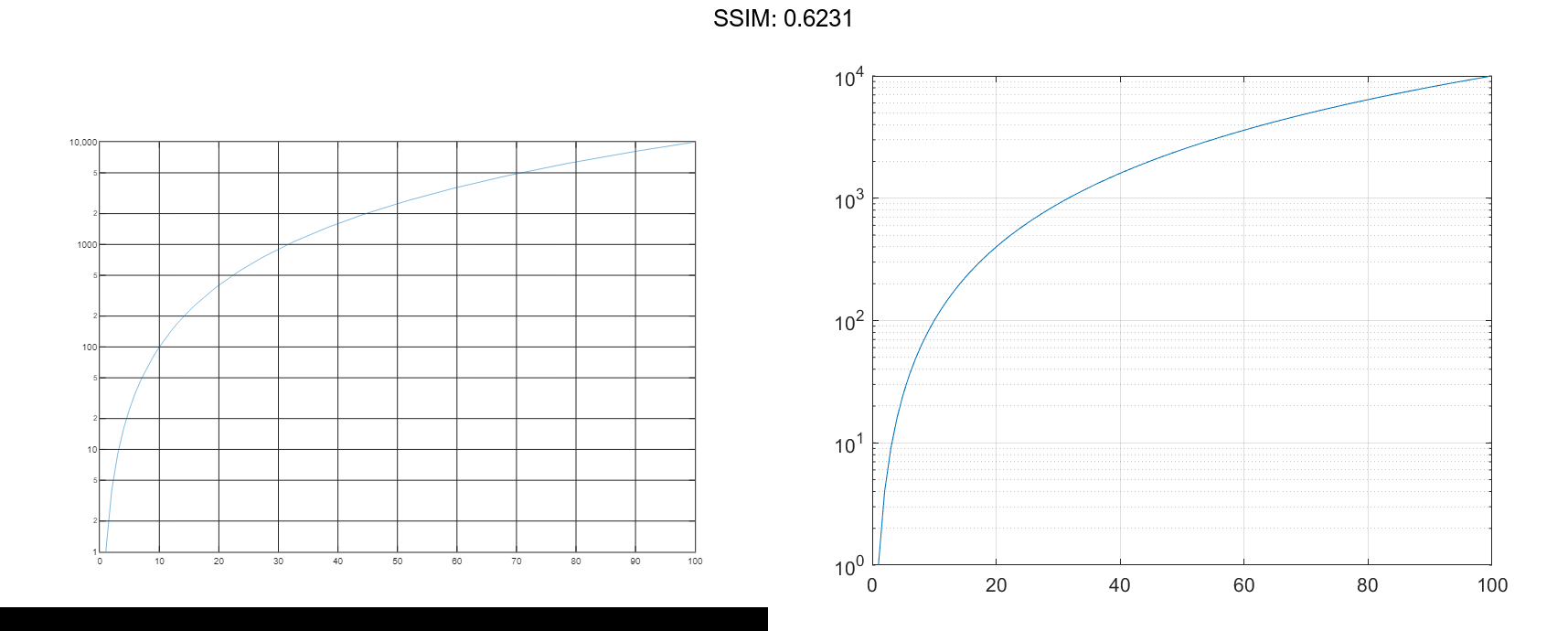
Plot One Line
Create a vector of x-coordinates and a vector of y-coordinates. Create a log-linear plot of x and y, and call the grid function to show the grid lines.
x = 1:100; y = x.^2; semilogy(x,y) grid on fig2plotly()

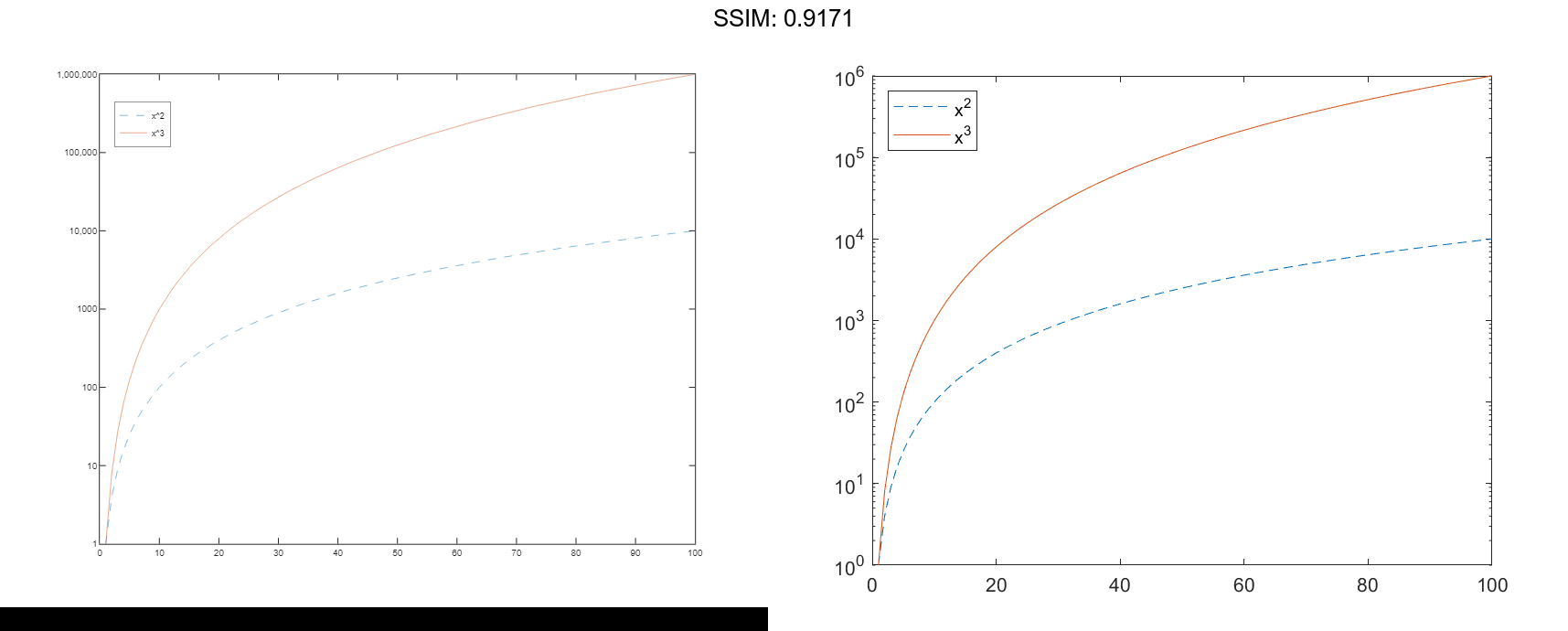
Plot Multiple Lines
Create a vector of x-coordinates and two vectors of y-coordinates. Plot two lines by passing comma-separated x-y pairs to semilogy.
x = 1:100; y1 = x.^2; y2 = x.^3; semilogy(x,y1,x,y2) grid on fig2plotly()


Specify Tick Locations, Tick Labels, and Axis Labels
Define vector x as the installments on a 20 year loan. Define vector y as the cumulative cost of a $1000 loan with an interest rate of 8%. Plot the cumulative cost at each installment.
P = 1000; npayments = 240; rate = 0.08/12; mpayment = P*(rate*(1+rate)^npayments)/(((1+rate)^npayments) - 1); x = 1:240; y = x * mpayment; semilogy(x,y); grid on fig2plotly()


Change the y-axis tick values and tick labels by calling the yticks and yticklabels functions. Then create x- and y-axis labels by calling the xlabel and ylabel functions.
yticks([10 50 100 500 1000])
yticklabels({'$10','$50','$100','$500','$1000'})
xlabel ('Installment')
ylabel('Cumulate Cost')
fig2plotly()


Plot Points as Markers Without Lines
Create a set of x- and y-coordinates and plot them in a log-linear plot. Specify the line style as 'o' to display circular markers without connecting lines. Specify the marker fill color as the RGB triplet [0 0.447 0.741], which corresponds to a dark shade of blue.
x = linspace(1,1000,15); y = (1./x) * 10000; semilogy(x,y,'o','MarkerFaceColor',[0 0.447 0.741]) grid on fig2plotly()


Add a Legend
Create two sets of x- and y-coordinates and display them in a log-linear plot. Specify a dashed line for the first set of coordinates. Then display a legend in the upper left corner of the plot by calling the legend function and specifying the location as 'northwest'.
x = 1:100;
y1 = x.^2;
y2 = x.^3;
semilogy(x,y1,'--',x,y2)
legend('x^2','x^3','Location','northwest')
fig2plotly()

Specify y-Coordinates Only
When you specify only one coordinate vector, semilogy plots those coordinates against the values 1:length(y). For example, define y as a vector of 5 values. Create a log-linear plot of y.
y = [0.1 0.2 1 10 1000]; semilogy(y) grid on fig2plotly()


If you specify y as a matrix, the columns of y are plotted against the values 1:size(y,1). For example, define y as a 5-by-3 matrix and pass it to the semilogy function. The resulting plot contains 3 lines, each of which has x-coordinates that range from 1 to 5.
y = [ 0.1 1 10
0.2 2 20
1.0 10 100
10 100 1000
1000 10000 100000];
semilogy(y)
grid on
fig2plotly()


Specify Target Axes
Create a tiled chart layout in the 'flow' tile arrangement, so that the axes fill the available space in the layout. Next, call the nexttile function to create an axes object and return it as ax1. Then display a log-linear plot by passing ax1 to the semilogy function.
tiledlayout('flow')
ax1 = nexttile;
x = 1:100;
y1 = x.^2;
semilogy(ax1,x,y1)
fig2plotly()


Repeat the process to create a second log-linear plot.
ax2 = nexttile; y2 = 1./x; semilogy(ax2,x,y2) fig2plotly()


Change Line Appearance After Plotting
Create a log-linear plot containing two lines, and return the line objects in the variable slg.
x = 1:100; y1 = x.^2; y2 = x.^3; slg = semilogy(x,y1,x,y2);


Change the width of the first line to 3, and change the color of the second line to purple.
slg(1).LineWidth = 3; slg(2).Color = [0.4 0 1]; fig2plotly()


Plot Discontinuous Function
Insert NaN values wherever there are discontinuities in your data. The semilogy function displays gaps at those locations.
Create a pair of x- and y-coordinate vectors. Replace the twentieth y-coordinate with a NaN value. Then create a log-linear plot of x and y.
x = 1:50; y = x.^2; y(20) = NaN; semilogy(x,y) fig2plotly()



